Answer:
The fugacity coefficient is
![[(f)/(p) ] = 1.45](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/swyea527kal8xiz8u62zs64epnn6n8pquh.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The gas obeys the equation
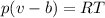
The value of b is
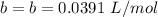
The pressure is
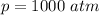
The temperature is
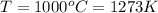
generally
![RT ln[(f)/(p) ] = \int\limits^(p)_(o) [ {v_(r) -v_(i)} ]\, dp](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5q8djxs8r2q2c55d273q2jab8mq4cgj987.png)
Where
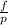 is the fugacity coefficient
is the fugacity coefficient
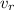 is the real volume which is mathematically evaluated from above equation as
is the real volume which is mathematically evaluated from above equation as
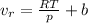
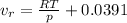
and
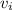 is the ideal volume which is evaluated from the ideal gas equation (pv = nRT , at n= 1) as
is the ideal volume which is evaluated from the ideal gas equation (pv = nRT , at n= 1) as
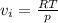
So
![RT ln[(f)/(p) ] = \int\limits^(1000)_(o) [[ (RT)/(p) + 0.0391] - [(RT)/(p) ]} ]\, dp](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bvbribltzgq4ez4y3y34la2jxc9a5b8fln.png)
=>
![RT ln[(f)/(p) ] = \int\limits^(1000)_(o) [0.391 ]\, dp](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5llxhpnclnu333qgcknwl60xtdxczwcxjw.png)
=>
![RT ln[(f)/(p) ] = [0.391p]\left | 1000} \atop {0}} \right.](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/15958bnanoqxv3w3q8sd1xrqwll2at4z6v.png)
=>
![RT ln[(f)/(p) ] = 38.1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bwvsvgtyoyifi1uep4gy2ngd140wcv47yg.png)
So
![ln[(f)/(p) ] = (39.1)/(RT)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g3rtloqlqgxlrx7qek6p0gd982seta2oac.png)
Where R is the gas constant with value
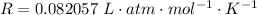
![[(f)/(p) ] = (39.1)/( 2.303 *0.082057 * 1273)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qvflwj39e4hu2wsr3bnpx0xilfqb5aqrd5.png)
![[(f)/(p) ] = 1.45](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/swyea527kal8xiz8u62zs64epnn6n8pquh.png)