Answer:
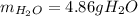
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the described chemical reaction is:
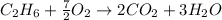
Thus, for the given reacting masses, we must identify the limiting reactant for us to determine the maximum mass of water that could be produced, therefore, we proceed to compute the available moles of ethane:
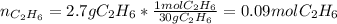
Next, we compute the moles of ethane consumed by 13.0 grams of oxygen by using the 1:7/2 molar ratio between them:
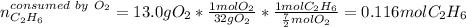
Thus, we notice there are less available moles of ethane, for that reason, it is the limiting reactant, thereby, the maximum amount of water is computed by considering the 1:3 molar ratio between ethane and water:
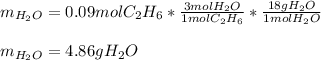
Best regards.