Answer:
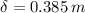 (Compression)
(Compression)
Step-by-step explanation:
The aluminium bar is experimenting a compression due to an axial force, that is, a force exerted on the bar in its axial direction. (See attachment for further details) Under the assumption of small strain, the deformation experimented by the bar is equal to:
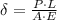
Where:
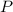 - Load experimented by the bar, measured in newtons.
- Load experimented by the bar, measured in newtons.
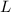 - Length of the bar, measured in meters.
- Length of the bar, measured in meters.
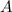 - Cross section area of the bar, measured in square meters.
- Cross section area of the bar, measured in square meters.
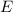 - Elasticity module, also known as Young's Module, measured in pascals, that is, newtons per square meter.
- Elasticity module, also known as Young's Module, measured in pascals, that is, newtons per square meter.
The cross section area of the bar is now computed: (
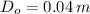 ,
,
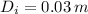 )
)
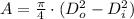
Where:
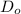 - Outer diameter, measured in meters.
- Outer diameter, measured in meters.
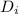 - Inner diameter, measured in meters.
- Inner diameter, measured in meters.
![A = (\pi)/(4)\cdot [(0.04\,m)^(2)-(0.03\,m)^(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/xuso4cmcy89suef7rl6r0jd1zu3w8rmnc1.png)
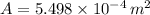
The total contraction of the bar due to compresive load is: (
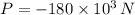 ,
,
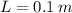 ,
,
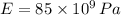 ,
,
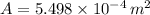 ) (Note: The negative sign in the load input means the existence of compressive load)
) (Note: The negative sign in the load input means the existence of compressive load)
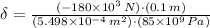
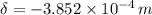
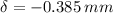
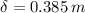 (Compression)
(Compression)