Answer:
Explanation:
a)
Class limits Frequency
38 - 63 9
64 - 89 7
90 - 115 1
116 - 141 1
142 - 167 2
Construct a histogram of these data(image attached)
b)
Frequency distribution table (also known as frequency table) consists of various components.
Classes: A large number of observations varying in a wide range are usually classified in several groups according to the size of their values. Each of these groups is defined by an interval called class interval. The class interval between 10 and 20 is defined as 10-20.
Class limits: The smallest and largest possible values in each class of a frequency distribution table are known as class limits. For the class 10-20, the class limits are 10 and 20. 10 is called the lower class limit and 20 is called the upper class limit.
Class limit: Class limit is the midmost value of the class interval. It is also known as the mid value.
Mid value of each class = (lower limit + Upper limit)2.
If the class is 38 to 63 , lower limit is 38 and upper limit is 63. So the mid value is
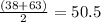
Class width is calculated using upper and lower value
Class width = (upper - lower) value /class
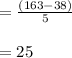
Magnitude of a class interval: The difference between the upper and lower limit of a class is called the magnitude of a class interval.
Class frequency: The number of observation falling within a class interval is called class frequency of that class interval.