Answer:
The new volume is 0.015 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's Law is a gas law that relates the pressure and volume of a certain amount of gas, without temperature variation, that is, at constant temperature.
Boyle's law says:
"The volume occupied by a given gas mass at constant temperature is inversely proportional to the pressure"
That is to say that if the pressure increases, the volume decreases and if the pressure decreases, the volume increases.
Boyle's law is expressed mathematically as:
Pressure * Volume = constant
or P * V = k
If a change in pressure or volume occurs at a constant temperature, the following is true:
P1*V1 = P2*V2
Where P1 and V1 are the pressure and volume in state 1 and P2 and V2 are the pressure and volume in state 2.
That is, the product between the initial pressure and the initial volume is equal to the product of the final pressure times the final volume.
In this case:
- P1= 101.3 kPa=101,300 Pa (being 1 kPa=1,000 Pa)
- V1= 30 mL= 0.03 L (1 L= 1,000 mL)
- P2= 202.6 kPa=202,600 Pa
- V2= ?
Replacing:
101,300 Pa*0.03 L=202,600 Pa* V2
Solving:
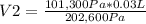
V2= 0.015 L
The new volume is 0.015 L