Answer:
a) 1.6*10^6 V
b) 13.35*10^6 V
Step-by-step explanation:
The electric potential at origin is the sum of the contribution of the two charges. You use the following formula:
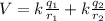 (1)
(1)
q1 = 3.90µC = 3.90*10^-6 C
q2 = -2.4µC = -2.4*10^-6 C
r1 = 1.25 cm = 0.0125 m
r2 = -1.80 cm = -0.018 m
k: Coulomb's constant = 8.98*10^9 Nm^2/C^2
You replace all the parameters in the equation (1):
![V=k[(q_1)/(r_1)+(q_2)/(r_2)]\\\\V=(8.98*10^9Nm^2/C^2)[(3.90*10^(-6)C)/(0.0125m)+(-2.4*10^(-6)C)/(0.018m)]=1.6*10^6V](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/x7ky3br2k1ikaf218ti6jn5qmw6036iepn.png)
hence, the total electric potential is approximately 1.6*10^6 V
b) For the coordinate (1.50 cm , 0) = (0.015 m, 0) you have:
r1 = 0.0150m - 0.0125m = 0.0025m
r2= 0.015m + 0.018m = 0.033m
Then, you replace in the equation (1):
![V=(8.98*10^9Nm^2/C^2)[(3.90*10^(-6)C)/(0.0025m)+(-2.4*10^(-6)C)/(0.033m)]=13.35*10^6V](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/b5u0iu5t8fsjoxffald42uzmg63dga2b9i.png)
hence, for y = 1.50cm you obtain V = 13.35*10^6 V