Step-by-step explanation:
main equation we need is
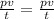
for Work done the equation is
W = P . ∆V (for isobar or constant pressure and isovolume or constant volume)
W = nRT ln V2/V1 (for isothermal or constant temperature)
p = pressure
v = volume
t = temperature (in Kelvin)
w = work
t = 27° C = 300 K
a. constant volume means ∆V (change on volume) is 0. So the work done in this process is 0
b. constant pressure (using SI unit)
W = P . ∆V = 2 . 1.01 . 10⁵ Pa . (12 - 3) . 10-³ m³ = 1 818 Joule
c. it's not clear in what operation in this process. but we can assume the process same with b (because if we will use constant temperature, there isn't any number for mol n) so
W = P . ∆V = 2 . 1.01 . 10⁵ Pa . (6 - 3) . 10-³ m³ = 606 Joule
hope this can help you