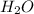Answer: The right conjugate of
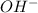 is
is
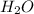
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base theory, an acid is defined as a substance which looses donates protons and thus forming conjugate base and a base is defined as a substance which accepts protons and thus forming conjugate acid.
For the given chemical equation:
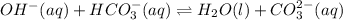
Here,
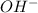 is gaining a proton, thus it is considered as a brønsted-lowry base and after gaining a proton, it forms
is gaining a proton, thus it is considered as a brønsted-lowry base and after gaining a proton, it forms
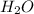 which is a conjugate acid.
which is a conjugate acid.
Thus the right conjugate of
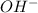 is
is