Answer:
The explanation of the given scenario is described in the explanation section below.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given values are:
Selling Price, SP = $0.92
AP = $0.85
(1)...
To compute the flexible budget variance,
=
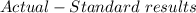
=
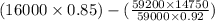
=
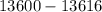
= $
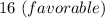
(2)...
To compute the price and efficiency variances,
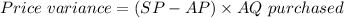
⇒
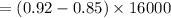
⇒
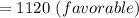
Now,
Efficiency variance = (SQ for actual output - AQ ) × SP
⇒ =
![( [(59200* 14750 )/(59000) ] - 16000 )* 0.92](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/business/college/fay6mgmtnr9lcqq843168lfzx6fxahvftc.png)
⇒ =
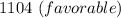
(3)...
The Price variance is the difference that further tends to mean that the material was bought at such a cheaper rate than assumed, but the efficiency variance does seem to be unfavorable, which tends to mean that the content has been used more than anticipated. Yet another possible explanation for that kind of variance could be lower prices contribute to better customer satisfaction,
However, the overall variance seems to be $16 favorable, and therefore final figures could be said to satisfy the requirements.