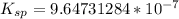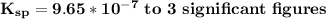Answer:
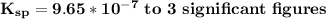
Step-by-step explanation:
Dissociation of Ca(IO₃)₂ is as follows:
Ca(IO₃)₂ ⇄ Ca²⁺ + 2IO₃⁻
This implies that for every mole of Ca(IO₃)₂ that dissolves in water' 1 mole of Ca²⁺ is obtained and 2 moles of IO₃⁻ is obtained.
The solubility in mol/L when Ca(IO₃)₂ is added to KIO₃ = 0.00341
Concentration of Ca²⁺ will be = 0.00341 M ˣ 1 = 0.00341 M ( i.e equal to the solubility of Ca(IO₃)₂)
Concentration of IO₃⁻ will be = 0.00341 M ˣ 2 = 0.00682 M
IO₃⁻ is also obtained from the dissociation of KIO₃ in water. the IO₃⁻ obtained from this process is = 0.01 M
The total concentration of IO₃⁻ now = 0.00682 M + 0.01 M = 0.01682 M
The solubility product
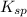 can be calculated by the formula:
can be calculated by the formula:
![K_(sp) = [Ca^(2+)][IO^-_3]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gr5pfhj9abtp0xbmb5tpqip4y0semzksu9.png)
![K_(sp) = [0.00341][0.01682]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mkh1b8qgshzgb7ju7wwopd2eap21cffvl1.png)
![K_(sp) = [0.00341][2.829124*10^(-4)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/w75mmm9ubsp3f98fi2cmknm2h0a3eudbso.png)