Answer:
The steady-state temperature is
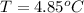
Yes it is chilly
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told
The intensity of solar radiation is
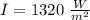
Generally the Stefan Boltzmann Law is mathematically represented as
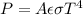
Where
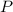 is the total power radiated
is the total power radiated
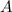 is the surface area of the object
is the surface area of the object
 is the emissivity
is the emissivity
T is the temperature of the object
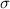 is the Boltzmann constant with a value
is the Boltzmann constant with a value
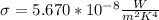
Generally at steady state the input power to the object is equal to the output power from the object
i.e
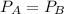
Now
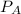
which is the input power to the object is not dependent on the object temperature and on the Boltzmann constant
thus
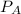 is mathematically represented as
is mathematically represented as
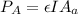
Where
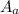 is absorptive surface area mathematically represented as
is absorptive surface area mathematically represented as
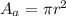
Thus
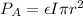
And
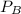 which is the output power to the object is mathematically represented a
which is the output power to the object is mathematically represented a
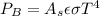
Where
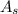 is the radiative surface area which is mathematically as
is the radiative surface area which is mathematically as
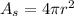
So
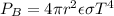
=>
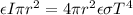
=>
![T = \sqrt[4]{(I)/(4 \sigma ) }](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/mo6368of4am0v11u0i0391pz725b4emh2f.png)
substituting values
![T = \sqrt[4]{(1370)/(4 * 5.670 *10^(-8) ) }](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/8i4v2uqyf3547ynt1eacebv455r5dqq73c.png)
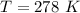
Converting to degrees
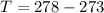
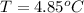
This implies that at steady state it is chilly