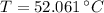Answer:
The final temperature of the water when thermal equilibrium is reached is 52.061 °C.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, which is a generalization of the Principle of Energy Conservation, energy cannot be created nor destroyed. In this case, ice enters in hot water and hot water releases heat until both elements reach thermal equilibrium. The consideration of an isolated system means the inexistence of any mass and energy interactions between system and surroundings.
Empirically speaking, ice is melt and reaches thermal equilibrium with rest of water. The system experiments the following changes:
1) Ice is melt and turns into water before reaching thermal equilibrium. (Positive change in internal energy)
2) Hot water is cooled before reaching thermal equilibrium. (Negative change in internal energy)
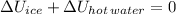
Change in internal energy in solids and liquids is equal to:
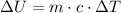
Where:
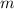 - Mass of the sample, measured in kilograms.
- Mass of the sample, measured in kilograms.
 - Specific heat, measured in
- Specific heat, measured in
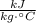 .
.
 - Change in temperature, measured in
- Change in temperature, measured in
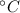 .
.
Besides, change in internal energy associated with phase changes is equal to:
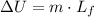
Where
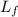 is the latent heat of fussion, measured in
is the latent heat of fussion, measured in
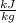 .
.
Then, previous energy equation is expanded as follows:
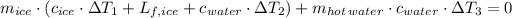
Inputs are described below:
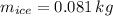 ,
,
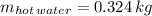 ,
,
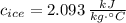 ,
,
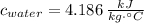 ,
,
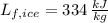
Temperature changes are:
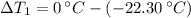
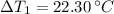
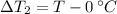
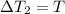
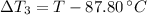
After replacing known variables and simplifying resulting expression, the following expression is found:
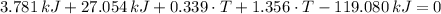
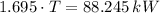
Finally, the final temperature of the water when thermal temperature is reached is: