Answer:
Use for the conversion to
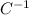 the same value as you have for the thermal expansion in
the same value as you have for the thermal expansion in

Explanation:
Start from the equation that relates Kelvin to degree Celsius
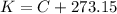
So notice that this is a linear relationship which involves the fact that an increase in Celsius temperature is the same as an increase in Kelvin. The important fact here is that the actual temperature change is the same in both scales because in the linear relationship above, the variable C has multiplicative factor 1 (one) and not other number.
If the temperature in C raises 15 degrees for example, the Kelvin measure also raises 15:
(C+15) +273.15 = C + 273.15 + 15 = K + 15
This is important because the coefficient of thermal linear expansion is defined as the "change in length of a solid per unit length and per unit change in temperature".
Therefore, the value you have for a thermal expansion in units of
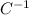 , is the same value you use is expressing the thermal expansion in
, is the same value you use is expressing the thermal expansion in
 .
.