Answer:
The rate of change of the bottom of the ladder is 4 feet per second.
Explanation:
Let be
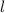 the length of the ladder,
the length of the ladder,
 the horizontal distance from the bottom of the ladder to the wall and
the horizontal distance from the bottom of the ladder to the wall and
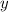 the vertical distance from the top of the ladder to the floor. Besides, let is assume that wall is perpendicular to floor. The geometry associated with the ladder can be modelled after the Pythagorean Theorem:
the vertical distance from the top of the ladder to the floor. Besides, let is assume that wall is perpendicular to floor. The geometry associated with the ladder can be modelled after the Pythagorean Theorem:
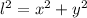
Rate of change in time experimented by the ladder is found after deriving the previous formula:
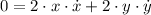
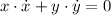
Besides,
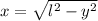
Then,
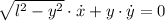
Now, the rate of change of the horizontal distance is cleared in the expression:
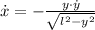
Given that
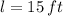 ,
,
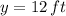 and
and
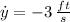 (as top of the ladder is sliding down), the rate of change of the bottom of the ladder is:
(as top of the ladder is sliding down), the rate of change of the bottom of the ladder is:
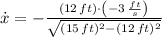
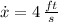
The rate of change of the bottom of the ladder is 4 feet per second.