Answer:
f1 ( x ) valid pdf . f2 ( x ) is invalid pdf
k = 1 / 18 , i ) 0.6133 , ii ) 0.84792
Explanation:
Solution:-
A) The two pdfs ( f1 ( x ) and f2 ( x ) ) are given as follows:
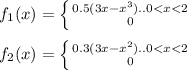
- To check the legitimacy of a continuous probability density function the area under the curve over the domain must be equal to 1. In other words the following:
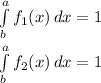
- We will perform integration of each given pdf as follows:
![\int\limits^a_b {f_1(x)} \, dx = \int\limits^2_0 {0.5(3x - x^3 )} \, dx \\\\\int\limits^a_b {f_1(x)} \, dx = [ 0.75x^2 - 0.125x^4 ]\limits^2_0\\\\\int\limits^a_b {f_1(x)} \, dx = [ 0.75*(4) - 0.125*(16) ]\\\\\int\limits^a_b {f_1(x)} \, dx = [ 3 - 2 ] = 1\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/m2ejz5ojtzqaxtrxfk3pa0ipzcm8soby3p.png)
![\int\limits^a_b {f_2(x)} \, dx = \int\limits^2_0 {0.5(3x - x^2 )} \, dx \\\\\int\limits^a_b {f_1(x)} \, dx = [ 0.75x^2 - (x^3)/(6) ]\limits^2_0\\\\\int\limits^a_b {f_1(x)} \, dx = [ 0.75*(4) - ((8))/(6) ]\\\\\int\limits^a_b {f_1(x)} \, dx = [ 3 - 1.3333 ] = 1.67 \\eq 1 \\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/pluby4taoxuwub6y126ewy0xd5f3xi4b3v.png)
Answer: f1 ( x ) is a valid pdf; however, f2 ( x ) is not a valid pdf.
B)
- A random variable ( X ) denotes the resistance of a randomly chosen resistor, and the pdf is given as follows:
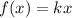 if 8 ≤ x ≤ 10
if 8 ≤ x ≤ 10
0 otherwise.
- To determine the value of ( k ) we will impose the condition of validity of a probability function as follows:
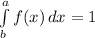
- Evaluate the integral as follows:
![\int\limits^1_8 {kx} \, dx = 1\\\\(kx^2)/(2) ]\limits^1^0_8 = 1\\\\k* [ 10^2 - 8^2 ] = 2\\\\k = (2)/(36) = (1)/(18)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ykm7kvabu3os5gu4vfk86sbsozmfq9q4vt.png) ... Answer
... Answer
- To determine the CDF of the given probability distribution we will integrate the pdf from the initial point ( 8 ) to a respective value ( x ) as follows:
![cdf = F ( x ) = \int\limits^x_8 {f(x)} \, dx\\\\F ( x ) = \int\limits^x_8 {(x)/(18) } \, dx\\\\ F ( x ) = [ (x^2)/(36) ] \limits^x_8\\\\F ( x ) = (x^2 - 64)/(36)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/v6tcylbeclaum5k2wsdlhpf8oyn1dmkc9j.png)
To determine the probability p ( 8.6 ≤ x ≤ 9.8 ) we will utilize the cdf as follows:
p ( 8.6 ≤ x ≤ 9.8 ) = F ( 9.8 ) - F ( 8.6 )
p ( 8.6 ≤ x ≤ 9.8 ) =
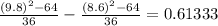
ii) To determine the conditional probability we will utilize the basic formula as follows:
p ( x ≤ 9.8 | x ≥ 8.6 ) = p ( 8.6 ≤ x ≤ 9.8 ) / p ( x ≥ 8.6 )
p ( x ≤ 9.8 | x ≥ 8.6 ) = 0.61333 / [ 1 - p ( x ≤ 8.6 ) ]
p ( x ≤ 9.8 | x ≥ 8.6 ) = 0.61333 / [ 1 - 0.27666 ]
p ( x ≤ 9.8 | x ≥ 8.6 ) = 0.61333 / [ 0.72333 ]
p ( x ≤ 9.8 | x ≥ 8.6 ) = 0.84792 ... answer