Answer:
Here's what I get.
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Brønsted-Lowry theory
An acid is a substance that can donate a proton to another substance.
A base is a substance that can accept a proton from another substance.
2. pH of ammonia
The chemical equation is
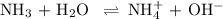
For simplicity, let's re-write this as
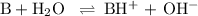
(a) Set up an ICE table.
B + H₂O ⇌ BH⁺ + OH⁻
I/mol·L⁻¹: 0.335 0 0
C/mol·L⁻¹: -x +x +x
E/mol·L⁻¹: 0.335 + x x x
![\rm K_{\text{b}} = \frac{\text{[BH}^(+)]\text{[OH}^(-)]}{\text{[B]}} = 1.8 * 10^(-5)\\\\(x^(2))/(0.335 - x) = 1.8 * 10^(-5)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ogyotsuyi82nqi73ud1e9b100oyu1d97t6.png)
Check for negligibility:
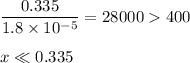
(b) Solve for [OH⁻]
![(x^(2))/(0.335) = 1.8 * 10^(-5)\\\\x^(2) = 0.335 * 1.8 * 10^(-5)\\x^(2) = 6.03 * 10^(-6)\\x = \sqrt{6.03 * 10^(-6)}\\x = \text{[OH]}^(-) = \mathbf{2.46 * 10^(-3)} \textbf{ mol/L}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hl95qkgu7hxhh3bn91fbkzggodome7q984.png)
(c) Calculate the pOH
![\text{pOH} = -\log \text{[OH}^(-)] = -\log(2.46 * 10^(-3)) = 2.61](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/jqrxo9lkq4ha28rypkrqr9r2438w03n6e7.png)
(d) Calculate the pH
pH = 14.00 - pOH = 14.00 - 2.61 = 11.39