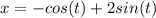Answer:
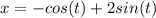
Explanation:
The problem is very simple, since they give us the solution from the start. However I will show you how they came to that solution:
A differential equation of the form:
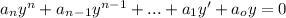
Will have a characteristic equation of the form:
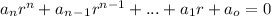
Where solutions
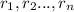 are the roots from which the general solution can be found.
are the roots from which the general solution can be found.
For real roots the solution is given by:
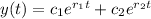
For real repeated roots the solution is given by:
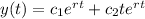
For complex roots the solution is given by:
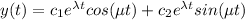
Where:
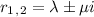
Let's find the solution for
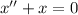 using the previous information:
using the previous information:
The characteristic equation is:
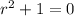
So, the roots are given by:
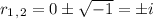
Therefore, the solution is:
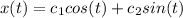
As you can see, is the same solution provided by the problem.
Moving on, let's find the derivative of
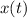 in order to find the constants
in order to find the constants
 and
and
 :
:
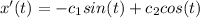
Evaluating the initial conditions:
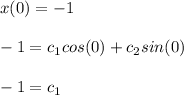
And
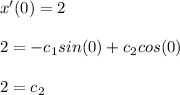
Now we have found the value of the constants, the solution of the second-order IVP is: