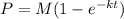Answer:
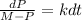
And we can integrate both sides of the equation using the following substitution:
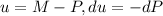
And replacing we got:
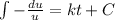
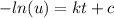
If we multiply both sides by -1 we got:
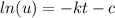
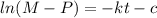
And using exponential in both sides of the equation we got:
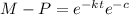
And solving for P we got:
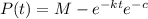
And replacing
 we got:
we got:
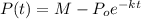
We can use the condition
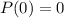 and we got:
and we got:
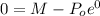
And we see that
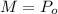 and replacing we got:
and replacing we got:
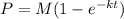
Explanation:
For this case we aasume the following differential equation:
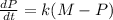
Is a separable differential equation so we can do the following procedure:
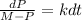
And we can integrate both sides of the equation using the following substitution:
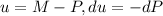
And replacing we got:
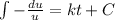
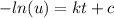
If we multiply both sides by -1 we got:
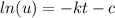
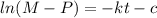
And using exponential in both sides of the equation we got:
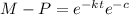
And solving for P we got:
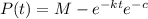
And replacing
 we got:
we got:
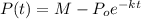
We can use the condition
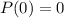 and we got:
and we got:
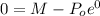
And we see that
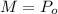 and replacing we got:
and replacing we got: