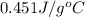Answer : The specific heat of the metal is,
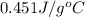
Explanation :
In this problem we assumed that heat given by the hot body is equal to the heat taken by the cold body.
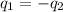
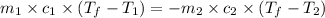
where,
 = specific heat of metal = ?
= specific heat of metal = ?
 = specific heat of water =
= specific heat of water =
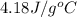
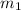 = mass of metal = 50.0 g
= mass of metal = 50.0 g
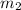 = mass of water = 125 g
= mass of water = 125 g
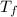 = final temperature of mixture =
= final temperature of mixture =
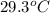
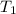 = initial temperature of metal =
= initial temperature of metal =
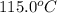
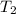 = initial temperature of water =
= initial temperature of water =
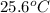
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get
![(50.0g)* c_1* (29.3-115.0)^oC=-[(125g)* 4.18J/g^oC* (29.3-25.6)^oC]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/3mjo0638ipsgu646tc2nlc6ajs3yug6r6f.png)
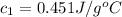
Therefore, the specific heat of the metal is,