Answer:
(-
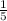 , 0 )
, 0 )
Explanation:
to find where the line crosses the x- axis, let y = 0 in the equation and solve for x
5x - 2(0) + 1 = 0
5x - 0 + 1 = 0
5x + 1 = 0 ( subtract 1 from both sides )
5x = - 1 ( divide both sides by 5 )
x = -
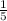
the line crosses the x- axis at (-
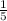 , 0 ) or ( - 0.2, 0 )
, 0 ) or ( - 0.2, 0 )