Answer:
P1 = 5.76 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the initial pressure of the gas you use the equation for ideal gases, for both temperatures and pressures:
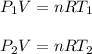
T1: initial temperature = 30°C = 303.15K
T2: final temperature = 45°C = 318.15K
P1: initial pressure = ?
P2: final pressure = 6atm
n: number of moles
R: ideal gas constant
The number of moles and R are constant, you can dive the first equation into the second and solve for P1:
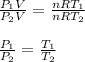
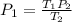
Finally, you replace the values of T1, P2 and T2:
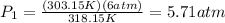
hence, the initial pressure of the gas was 5.71 atm