Answer:
4.75m^2
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:-
- Temperature of hot fluid at inlet:
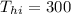 °C
°C
- Temperature of cold fluid at outlet:
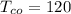 °C
°C
- Temperature of cold fluid at inlet:
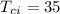 °C
°C
- The overall heat transfer coefficient: U = 1500 W / m^2 K
- The flow rate of cold fluid: m_c = 10,00 kg/ h
- The flow rate of hot fluid: m_h = 5,000 kg/h
Solution:-
- We will evaluate water properties at median temperatures of each fluid using table A-4.
Cold fluid: Tci = 35°C , Tco = 35°C
Tcm = 77.5 °C ≈ 350 K --- >

Hot fluid: Thi = 300°C , Tho = 150°C ( assumed )
Thm = 225 °C ≈ 500 K --- >
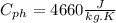
- We will use logarithmic - mean temperature rate equation as follows:

Where,
A_s : The surface area of heat exchange
ΔT_lm: the logarithmic differential mean temperature
q: The rate of heat transfer
- Apply the energy balance on cold fluid as follows:

- Similarly, apply the heat balance on hot fluid and evaluate the outlet temperature ( Tho ) :
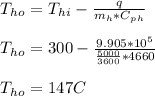
- We will use the experimental results of counter flow ( unmixed - unmixed ) plotted as figure ( Fig . 11.11 ) of the " The fundamentals to heat transfer" and determine the value of ( P , R , F ).
- So the relations from the figure 11.11 are:
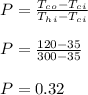
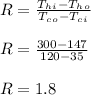
Therefore, P = 0.32 , R = 1.8 ---- > F ≈ 0.97
- The log-mean temperature ( ΔT_lm - cf ) for counter-flow heat exchange can be determined from the relation:
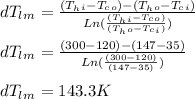
- The log - mean differential temperature for counter flow is multiplied by the factor of ( F ) to get the standardized value of log - mean differential temperature:

- The required heat exchange area ( A_s ) can now be calculated:
