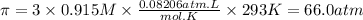Answer:
66.0 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
We can calculate the osmotic pressure (π) using the following expression.
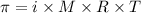
where,
Step 1: Calculate i
Sodium sulfate completely dissociates according to the following equation.
Na₂SO₄ ⇒ 2 Na⁺ + SO₄²⁻
Since it produces 3 ions, i = 3.
Step 2: Calculate M
We can calculate the molarity of Na₂SO₄ using the following expression.
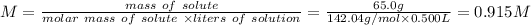
Step 3: Calculate T
We will use the following expression.
K = °C + 273.15
K = 20°C + 273.15 = 293 K
Step 4: Calculate π