Answer:
a) [COHNH₂] = 0.001 mol/L, [NH₃] = [CO] = 0.085 mol/L
b) 5.59 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The decomposition reaction of formamide is the following:
COHNH₂(d) ⇆ NH₃(g) + CO(g)
The equilibrium constant of the reaction above is:
![K_(c) = ([NH_(3)][CO])/([COHNH_(2)]) = 4.84 (400 K)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ilb931jx3i63ktjq6qzosbnbsqf5isndjf.png)
The initial concentration of formamide is:
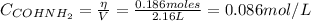
Where: η is the number of moles and V is the volume
Now, in the equilibrium the concentration of all species is:
COHNH₂(d) ⇆ NH₃(g) + CO(g)
0.086 - x x x
![K_(c) = ([NH_(3)][CO])/([COHNH_(2)]) = (x*x)/(0.086 - x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/k9tx02djfngb5903x53c32j4s8kt1jhm7h.png)
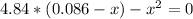
By solving the above equation for x we have:
x = 0.085 mol/L = [NH₃] = [CO]
[COHNH₂] = 0.086 - 0.085 = 0.001 mol/L
Therefore, the concentrations of all species present at equilibrium at 400 K is [NH₃] = [CO] = 0.085 mol/L and [COHNH₂] = 0.001 mol/L.
b) To find the total pressure in the container we need to find first the constant Kp as follows:
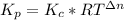
Where R is the gas constant = 0.082 Latm/(Kmol), T is the temperature = 400 K and Δn = 1
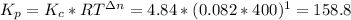
Now, the total pressure is:
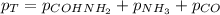
The pressure of COHNH₂ can be found using Ideal Gas Law:
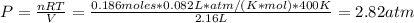
Using the equilibrium constant we can find the pressure of NH₃ and CO:
COHNH₂(d) ⇆ NH₃(g) + CO(g)
2.82 - x x x
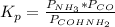
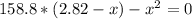
By solving the above equation for x we have:
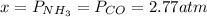
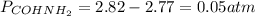
Thus, the total pressure is:
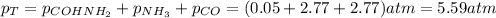
Hence, the total pressure in the container at equilibrium is 5.59 atm.
I hope it helps you!