Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
a )
from lens makers formula
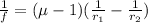
f is focal length , r₁ is radius of curvature of one face and r₂ is radius of curvature of second face
putting the values
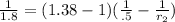
1.462 = 2 - 1 / r₂
1 / r₂ = .538
r₂ = 1.86 cm .
= 18.6 mm .
b )
object distance u = 25 cm
focal length of convex lens f = 1.8 cm
image distance v = ?
lens formula
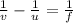
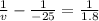
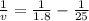
.5555 - .04
= .515
v = 1.94 cm
c )
magnification = v / u
= 1.94 / 25
= .0776
size of image = .0776 x size of object
= .0776 x 10 mm
= .776 mm
It will be a real image and it will be inverted.