Answer:
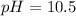
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the dissociation of the given weak acid is:
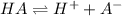
Therefore, the law of mass action for it turns out:
![Ka=([H^+][A^-])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/kzt7pcnoonz2fwfrgadywivsijtflo2dmk.png)
That in terms of the change
 due to the reaction extent is:
due to the reaction extent is:
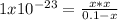
Thus, by solving with the quadratic equation or solver, we obtain:
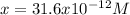
Which clearly matches with the hydrogen concentration in the solution, therefore, the pH is:
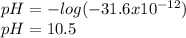
Regards.