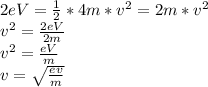Answer:
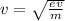
Step-by-step explanation:
The helium ion has:
a potential difference in vacuum = V,
Charge = 2e
and mass = 4m,
speed = v,
mass = 4m
From electrostatics, the work done is the product of charge and its potential difference.
Therefore, Work done = charge × potential difference = 2e × V = 2eV
This work done is in form of kinetic energy, therefore:
Kinetic energy = 1/2 × mass × speed²
⇒ Work done = Kinetic energy