Answer:
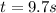
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, we have a second order kinetics given the second power of the concentration of chlorine (V) oxide in the rate expression, thus, the integrated equation for the concentration decay is:
![(1)/([Cl_2O_5])=kt+(1)/([Cl_2O_5]_0)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/fnqy2vdk8rs0gvpid9nprhntzissza3eih.png)
Thus, the final concentration for a 94% decrease is:
![[Cl_2O_5]=0.600M-0.600M*0.94=0.036M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5db0saapmu403xc0fows48d7zu3fcw7f5g.png)
Therefore, we compute the time for such decrease:
![kt=(1)/([Cl_2O_5])-(1)/([Cl_2O_5]_0)=(1)/(0.036M)-(1)/(0.60M) =26.1M^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jygvhhkcwubktfkpuekhwk0yxl0m0ougn3.png)
Regards.