Answer:
a. 50 turns
b. 0.0114 A
c. 0.25 A, 10 V
Explanation:
Given:-
- The required current ( Is ) = 0.5 A
- The required voltage ( Vs ) = 5 V
- Transformer is 100% efficient ( ideal )
- The number of turns in the primary coil, ( Np ) = 2200
- The Voltage generated by power station, ( Vp ) = 220 V
Find:-
a. The number of turns in the secondary coil of the transformer
b. The current supplied by the power station
c. The effect on output current and voltage when the number of turns of secondary coil are doubled.
Solution:-
- For ideal transformers that consists of a ferromagnetic core with two ends wounded by a conductive wire i.e primary and secondary.
- The power generated at the stations is sent to home via power lines and step-down before the enter our homes.
- A household receives a voltage of 220 V at one of it outlets. We are to charge a phone that requires 0.5 A and 5V for the process.
- The outlet and any electronic device is in junction with a smaller transformer.
- All transformers have two transformation ratios for current ( I ) and voltage ( V ) that is related to the ratio of number of turns in the primary and secondary.
Voltage Transformation =
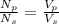
Where,
Ns : The number of turns in secondary winding
- Plug in the values and evaluate ( Ns ):
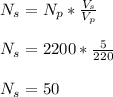
Answer a: The number of turns in the secondary coil should be Ns = 50 turns.
- Similarly, the current transformation is related to the inverse relation to the number of turns in the respective coil.
Current Transformation =
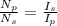
Where,
Ip : The current in primary coil
- Plug in the values and evaluate ( Ip ):
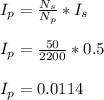
Answer b: The current in the primary coil should be Ip = 0.0114 Amp.
- The number of turns in the secondary coil are doubled . From the transformation ratios we know that that voltage is proportional to the number of turns in the respective coils. So if the turns in the secondary are doubled then the output voltage is also doubled ( assuming all other design parameters remains the same ). Hence, the output voltage is = 2*5V = 10 V
- Similary, current transformation ratio suggests that the current is inversely proportional to the number of turns in the respective coils. So if the turns in the secondary are doubled then the output current is half of the required ( assuming all other design parameters remains the same ). Hence, the output current is = 0.5*0.5 A = 0.25 A