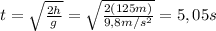Answer:
A) E = 2550 J
B) K = 1325 J
C) t = 5,05 s
Step-by-step explanation:
A) The total mechanical energy is given by the sum of the gravitational potential energy and the kinetic energy of the body:
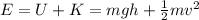 (1)
(1)
m: mass of the body = 2,0 kg
g: gravitational acceleration = 9,8 m/s^2
h: height = 125 m
v: initial velocity of the body = 10 m/s
You replace the values of all variables h, m, g and v in the equation (1):
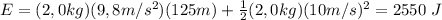
the total mechanical energy is 2550 J
B) The kinetic energy of the corp, when it is at a height of h/2 is given by:
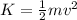
where
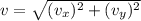
The x component of the velocity is constant in the complete trajectory, which is the initial velocity, that is, vo = vx
The y component is given by:
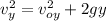
voy: vertical initial velocity = 0m/s
y: height = h/2 = 125/2 = 62.5 m
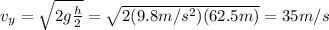
Then, you can calculate the velocity of the body and next, you can calculate the kinetic energy:
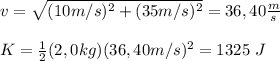
C) The time that body takes in all its trajectory is: