Answer:
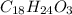
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, combustion analyses help us to determine the empirical formula of a compound via the quantification of the released carbon dioxide and water since the law of conservation of mass is leveraged to attain it. In such a way, as 36.86 g of carbon dioxide were obtained, this directly represents the mass of carbon present in the sample, thus, we first compute the moles of carbon:
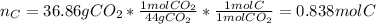
Then, into the water one could find the moles of hydrogen:
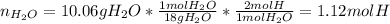
Now, we compute the moles of oxygen by firstly computing the mass of oxygen:
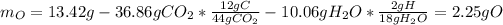
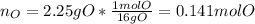
Then, we have the mole ratio:
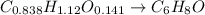
Whose molar mass is 12x6+1x8+16=96 g/mol, but the whole compound molar mass is 288.38, the factor is 288.38/96 =3, Therefore the formula:
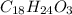
Regards.