Answer:
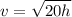
Step-by-step explanation:
The potential energy (PE) we are looking here is gravitational potential energy (GPE).
GPE= mgh,
where m is the mass of an object,
g is the gravitational field strength
h is the height of the object
KE= ½mv²,
where m is the mass and v is the velocity
loss in GPE= gain in KE
mgh= ½mv²
gh= ½v² (divide by m throughout)
Assuming that the object is on earth, then g= 10N/Kg
½v²= 10h (substitute g=10)
v²= 20h (×2 on both sides)
v= √20h (square root both sides)