Answer:
4.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since we are talking about the same material, their densities are the same:
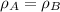
And each density is defined by:
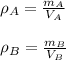
Thus, we also define the volume of a cylinder:
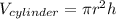
Therefore, we obtain:
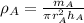
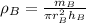
Now, the given information regarding the the length and the radius is written mathematically:
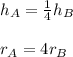
So we introduce such additional equations in:
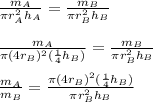
So we simplify for the radius and lengths:
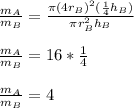
So the ratio of the mass of cylinder A to the mass of cylinder B is 4.
Best regards.