Answer:
0.00664 moles of solute are needed to prepare the solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is a unit of concentration based on the volume of a solution and is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. In other words, molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute that are dissolved in a given volume and is determined by the following expression:
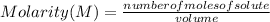
Molarity is expressed in units
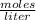 .
.
In this case:
- Molarity= 0.415 M
- number of moles of solute= ?
- volume= 16 mL= 0.016 L (being 1 L= 1000 mL)
Replacing:
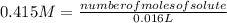
Solving:
number of moles of solute= 0.00664
0.00664 moles of solute are needed to prepare the solution.