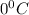26.3 grams of calcium carbonate must be decomposed to produce 5.00 L of carbon dioxide at 901 mmHg and
Step-by-step explanation:
According to ideal gas equation:
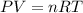
P = pressure of gas = 901 mm Hg = 1.18 atm (760 mm Hg = 1 atm)
V = Volume of gas = 5.00 L
n = number of moles = ?
R = gas constant =
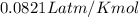
T =temperature =
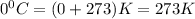
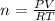
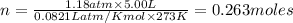
The chemical reaction for the decomposition of calcium carbonate follows the equation:
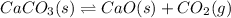
According to stoichiometry:
1 mole of carbon dioxide is produced by = 1 mole of calcium carbonate
Thus 0.263 moles of carbon dioxide is produced by =
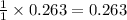 moles of calcium carbonate
moles of calcium carbonate
Mass of calcium carbonate=
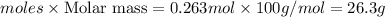
26.3 grams of calcium carbonate must be decomposed to produce 5.00 L of carbon dioxide at 901 mmHg and