Answer:
1) No, there is not enough evidence to support the claim that the vaccine was effective (P-value=0.104) .
The null and alternative hypothesis are:
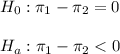
being the subindex 1 for the experimental group and subindex 2 for the control group.
2) Test statistic z=-1.26
Explanation:
This is a hypothesis test for the difference between proportions.
The claim is that the vaccine was effective.
Then, the null and alternative hypothesis are:
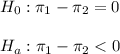
The significance level is 0.01.
The sample 1 (experimental group), of size n1=100000 has a proportion of p1=0.0002.
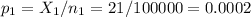
The sample 2 (control group), of size n2=100000 has a proportion of p2=0.0003.
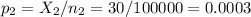
The difference between proportions is (p1-p2)=-0.0001.
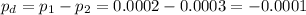
The pooled proportion, needed to calculate the standard error, is:
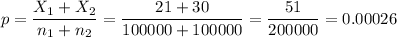
The estimated standard error of the difference between means is computed using the formula:
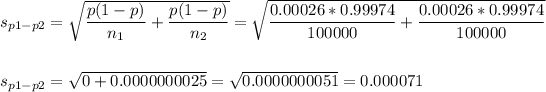
Then, we can calculate the z-statistic as:
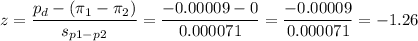
This test is a left-tailed test, so the P-value for this test is calculated as (using a z-table):
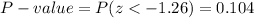
As the P-value (0.104) is bigger than the significance level (0.01), the effect is not significant.
The null hypothesis failed to be rejected.
There is not enough evidence to support the claim that the vaccine was effective.