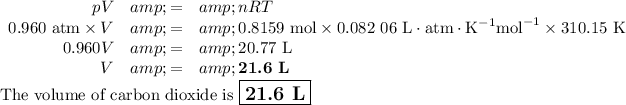Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
We must do the conversions
mass of C₆H₁₂O₆ ⟶ moles of C₆H₁₂O₆ ⟶ moles of CO₂ ⟶ volume of CO₂
We will need a chemical equation with masses and molar masses, so, let's gather all the information in one place.
Mᵣ: 180.16
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ ⟶ 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
m/g: 24.5
(a) Moles of C₆H₁₂O₆
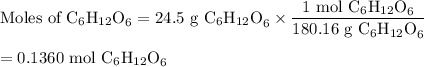
(b) Moles of CO₂
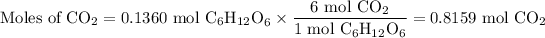
(c) Volume of CO₂
We can use the Ideal Gas Law.
pV = nRT
Data:
p = 0.960 atm
n = 0.8159 mol
T = 37 °C
(i) Convert the temperature to kelvins
T = (37 + 273.15) K= 310.15 K
(ii) Calculate the volume