Answer:
2.10 V
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the potential difference across the ends of the bar, you take into account that when the bar moves with speed v, in a constant magnetic field, the charges in the wire feels a magnetic force that separate the opposite charges, generating an induced potential difference given by the following formula:
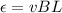 (1)
(1)
v: speed of the bar = 11.5 m/s
B: magnitude of the magnetic field = 1.22 T
L: length of the bar = 15.0cm = 0.15m
You replace the values of v, B and L in the equation (1):
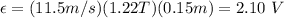
hence, the induced potential difference is 2.10 V