Answer:
The correct option is;
Cylinder A contains a gas that has a temperature closest to absolute zero
Step-by-step explanation:
From the kinetic theory of gases, the average speed of a gaseous molecule is found from the following equation;
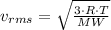
Where:
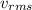 = rms speed which is the square root of the average of the velocities of the gas molecules squared which is used in place of the average of the gas molecules as the sum of the velocities of all the gas molecules in the cylinder is zero
= rms speed which is the square root of the average of the velocities of the gas molecules squared which is used in place of the average of the gas molecules as the sum of the velocities of all the gas molecules in the cylinder is zero
R = Universal gas constant = 8.3145 J/(mol·K)
MW = Molecular weight of the gas
Hence where we have;
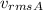 = Average velocity of gas A = 0.0000001 m/s
= Average velocity of gas A = 0.0000001 m/s
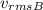 = Average velocity of gas B = 0.3 m/s
= Average velocity of gas B = 0.3 m/s
Since, R and MW are constant for the gas in cylinder A constant, therefore, as
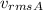 ≈ 0 m/s, the temperature,
≈ 0 m/s, the temperature,
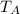 , of gas A is closest to absolute zero.
, of gas A is closest to absolute zero.