Answer:
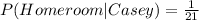
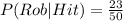
Explanation:
Hello!
1)
Given the table of probabilities you have to calculate the conditional probability that the result was a homeroom given that Casey was batting.
Following the general model you can calculate this probability as:
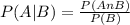
Given two events A and B that are not independent, the probability of A given that B has occurred is equal to the division between the intersection between A and B by the probability of B.
In terms of this excersise:
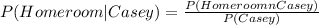
Reading the table, the "P(Casey)" is found on the marginals of the table, is calculated as the summation of all battings done by Casey:
P(Casey)= 0.1125+0.05+0.3375+0.025= 0.525
P(Homeroom∩Casey)= 0.025
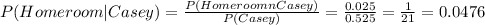
2)
You have to calculate the probability of the batting being made by Rob given that it was a hit.
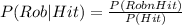
The probability of the intersection is
P(Rob∩Hit)= 0.2875
P(Hit)= 0.2875+0.3375= 0.625
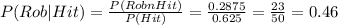
I hope this helps!