Answer:
Test statistic
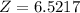
The Calculated value Z =6.5217 > 1.96 at 5% level of significance
Null hypothesis is rejected
There is real difference among all teens
Explanation:
Step(i):-
Given large sample size 'n' = 886
first sample proportion p⁻₁ = 44% =0.44
Second sample proportion p⁻₂ = 29% =0.29
Null hypothesis:H₀:There is no significant difference between two proportions
Alternative Hypothesis:H₁: There is significant difference between two proportions
Level of significance ∝ = 0.95 or 95%
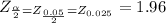
Step(ii):-
Test statistic
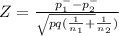
Where 'p'
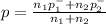
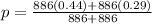
p = 0.365
q = 1-p =1-0.365 =0.635
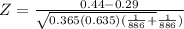
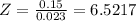
The Calculated value Z =6.5217 > 1.96 at 5% level of significance
Conclusion:-
Null hypothesis is rejected
There is real difference among all teens