Answer: The most likely partial pressures are 98.7MPa for NO₂ and 101.3MPa for N₂O₄
Explanation: To determine the partial pressures of each gas after the increase of pressure, it can be used the equilibrium constant Kp.
For the reaction 2NO₂ ⇄ N₂O₄, the equilibrium constant is:
Kp =
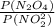
where:
P(N₂O₄) and P(NO₂) are the partial pressure of each gas.
Calculating constant:
Kp =
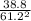
Kp = 0.0104
After the weights, the total pressure increase to 200 MPa. However, at equilibrium, the constant is the same.
P(N₂O₄) + P(NO₂) = 200
P(N₂O₄) = 200 - P(NO₂)
Kp =
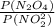
0.0104 =
![(200 - P(NO_(2)) )/([P(NO_(2) )]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/wmaodrd85ldu2aomr60wu6cd9cp0xu7y3y.png)
0.0104
![[P(NO_(2) )]^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/kc67ejsua80xzjtis3ldbzi20hdmln691o.png) +
+
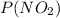 - 200 = 0
- 200 = 0
Resolving the second degree equation:
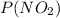 =
=
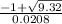
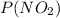 = 98.7
= 98.7
Find partial pressure of N₂O₄:
P(N₂O₄) = 200 - P(NO₂)
P(N₂O₄) = 200 - 98.7
P(N₂O₄) = 101.3
The partial pressures are
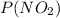 = 98.7 MPa and P(N₂O₄) = 101.3 MPa
= 98.7 MPa and P(N₂O₄) = 101.3 MPa