Answer:
299.11 A
Step-by-step explanation:
You first equal the magnetic force on the upper wire with the gravitational force:
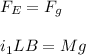 ( 1 ) (first term is the magnetic force produced by the magnetic force of the second wire)
( 1 ) (first term is the magnetic force produced by the magnetic force of the second wire)
i1: current of the upper wire
L: length
M: mass of the upper wire
B: magnetic field generated by the second wire
Next, you calculate the magnetic field produced by the other wire:
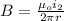 (2)
(2)
i2: current of the second wire
r: distance between wires
mo: magnetic permeability of vacuum = 4pi*10^-7 T/A
Next, you replace the expression (2) into the expression (1) in order to obtain an expression for i2:
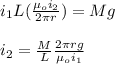
M/L = is the mass per unit length of the first wire
Finally, you replace the values of the parameters:
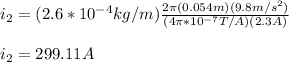
hence, the current in the second wire must be 299.11A