Answer:
The pressure is 2.696 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law relates pressure and volume inversely proportionally and is expressed mathematically as:
P * V = k
Charles's law consists of the relationship between the volume and temperature of a certain amount of ideal gas, which is maintained at a constant pressure, by means of a proportionality constant that is applied directly and is expressed mathematically as follows:
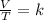
Gay-Lussac's law indicates that the gas pressure is directly proportional to its temperature and is expressed mathematically as:
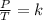
Combined law equation is the combination of three gas laws called Boyle's, Charlie's and Gay-Lusac's law:
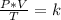
When you want to study two different states, an initial and a final one of a gas, you have the expression:
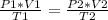
In this case, you know:
- P1=1 atm
- V1= 5 L
- T1= 20 °C=293° K (Being 0°C=273°K)
- P2=?
- V2= 2 L
- T2= 43 °C= 316°K
Replacing:
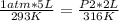
Solving:
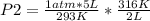
P2= 2.696 atm
The pressure is 2.696 atm