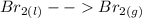Answer:
D. Homogeneous;Heterogeneous.
Step-by-step explanation:
Homogeneous equilibrium refers to a reaction in which the reactants and products are in the same phase i.e whether gaseous or liquid. This means it's concentration reactants and products in a chemical reaction can vary over a wide range.
For example,
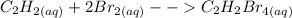
The Heterogeneous equilibrium refers to a reaction in which the reactants and products are in different phases i.e solid, gaseous, liquid or aqueous. Its position isn't dependent on the amounts of pure liquids or solids present in the reaction.
For example,