Answer:
The magnitude of the magnetic field halfway between the wires is 3.0 x 10⁻⁵ T.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
distance half way between the parallel wires, r = ¹/₂ (40 cm) = 20 cm = 0.2 m
current carried in opposite direction, I₁ and I₂ = 10 A and 20 A respectively
The magnitude of the magnetic field halfway between the wires can be calculated as;
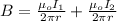
where;
B is magnitude of the magnetic field halfway between the wires
I₁ is current in the first wire
I₂ is current the second wire
μ₀ is permeability of free space
r is distance half way between the wires
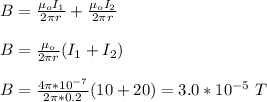
Therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic field halfway between the wires is 3.0 x 10⁻⁵ T.