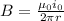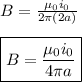Hi there!
Recall Ampere's Law:
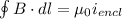
B = Magnetic Field Strength (T)
μ₀ = Permeability of Free Space (Tm/A)
i = Enclosed Current (A)
dL = differential path length
To begin, we must derive an expression for the magnetic field strength inside a wire that contains a uniformly-distributed current.
Using the expression:
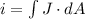
Where 'J' is the density of current, and A is the cross-sectional area:
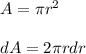
We know that:
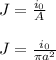
This is the current density. We can now integrate:
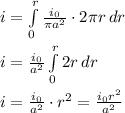
Now, substitute this expression back into the above equation for the magnetic field:
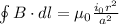
The path of integration is a closed loop of length 2πr, so:
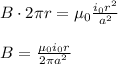
We can now use this equation for the first 2 parts.
a)
If 'r' equals 0:
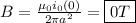
b)
If 'r' equals a/2:
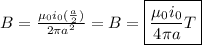
c)
At the wire's surface, 'r' = a:
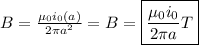
d)
At 'r' = 2a, since this is outside of the wire, the relationship between magnetic field and distance from the wire becomes a 1/r (inverse) relationship. This is found using Ampere's Law: