Answer:
576 N downward
Explanation:
I'm assuming by "resistance," the question is talking about the air resistance against it as it falls. As the box falls, it "battles" between the two opposing forces of air resistance (an upward force) and gravity (a downward force). We know the air resistance is 110N, but we still don't know what the force due to gravity is.
Newton's second law gives an equation for the acceleration on an object given its mass and the force acting upon it:
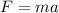
We know that the mass of our box is 70kg, but what's its downward accelaration? When you drop any object, it experiences some acceleration due to gravity. This acceleration depends on how large the mass accelerating it is, but on Earth, this value is roughtly 9.8 m/s² (you'll frequently see the letter g used as a label for this!) We can put this value into our equation, along with the mass of the box, to get our downward force:
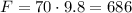
This means our box is experiencing 686 N of downward force.
Calculating the net force
The supply box is experiencing 110 N of upward force due to air resistance and 686 N of downward force due to gravity. Clearly, gravity wins out, so our net force will be directed downwards, but by how much? The upward force is going to cancel out some of the downward force, so we can subtract the 110 N of resistance from the 686 N of gravity to get a net force of
686 - 110 = 576 N downward