Answer:
D. 18,800 J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
We need to use the Arrhenius equation to solve for this problem:
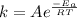 , where k is the rate constant, A is the frequency factor,
, where k is the rate constant, A is the frequency factor,
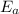 is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvins.
is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvins.
We want to find the value of
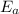 , so let's plug some of the information we have into the equation. The gas constant we can use here is 8.31 J/mol-K.
, so let's plug some of the information we have into the equation. The gas constant we can use here is 8.31 J/mol-K.
At 0°C, which is 0 + 273 = 273 Kelvins, the rate constant k is
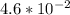 . So:
. So:
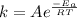
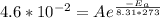
At 20°C, which is 20 + 273 = 293 Kelvins, the rate constant k is
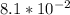 . So:
. So:
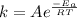
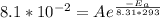
We now have two equations and two variables to solve for. We just want to find Ea, so let's write the first equation for A in terms of Ea:
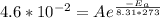
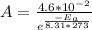
Plug this in for A in the second equation:
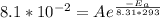
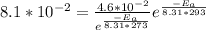
After some troublesome manipulation, the answer should come down to be approximately:
Ea = 18,800 J/mol
The answer is thus D.