Answer:
The experimental probability that the next child to enroll will be a preschooler is 40%
P(E) = 40%
Explanation:
What is Experimental Probability?
Experimental probability is basically the ratio of the number of outcomes occurred to the total number of trials in an actual experiment.
In this problem we are given that out of the last 10 children to enroll at the day care center, there are 4 children who belong to the category of preschoolers.
We are asked to find the experimental probability that the next child to enroll will be a preschooler.
The required experimental probability is given by
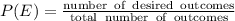
Where number of desired outcomes are 4 and total number of outcomes are 10
So the probability is
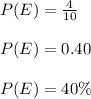
Therefore, the experimental probability that the next child to enroll will be a preschooler is 40%